A recent study in the Canadian Medical Association Journal found that 66% of processed foods contain at least one type of added sugar in the ingredients list. Registered Dietitian Sue Mah shared her thoughts on CBC News Network.
The study found that added sugars were present in products from baby food, baked goods and cereals to frozen dinners, snacks and yogurts.
Sugar, especially added sugar has been under fire for its association with health issues including heart disease, diabetes, dental cavities and obesity. Added sugars are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or beverages. This does not include naturally occurring sugars which are found in foods such as fruit, milk and yogurt.
The Heart and Stroke Foundation recommends limiting added sugars to a maximum of 10% of total calories in a day. For an average 2,000 calorie diet, 10% is about 48 grams or 12 teaspoons of added sugars a day.
In the USA, added sugars must be disclosed on nutrition labels by July 26, 2018. The situation differs here in Canada. Added sugars will not be disclosed on nutrition labels. Health Canada has set the % Daily Value (%DV) at 100 grams for total sugars (added sugars plus naturally occurring sugars).
Here’s my advice:
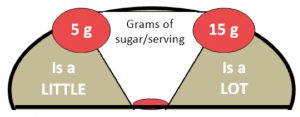
1. Read the Nutrition Facts table. Foods with 5 grams or less sugar per serving would be considered to have “a little” sugar whereas foods with 15 grams or more sugar per serving would be considered to have “a lot” of sugar.
2. Read the ingredients list. By 2021, different sugars will be identified individually and grouped together as “Sugars” on the ingredients list. In the meantime, look for ingredient names that indicate sugar or end in ‘ose’ which are sugars too (e.g. dextrose, glucose, fructose, maltose, sucrose).
3. Look at the whole food. Just because a food has little or no sugar doesn’t mean that it is a healthy or nutritious choice. Choose wholesome, foods for minimal sugar and maximum nutrition.

 Nutrition can sure be confusing! Here’s the truth about a few common nutrition myths.
Nutrition can sure be confusing! Here’s the truth about a few common nutrition myths. 